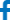
Production Process
Production Process
Raw materials
Reaction
Reaction 2
Reaction 3
Monitoring
Quantitative production
The production process of medical intermediate materials is a complex and delicate chemical synthesis process involving multiple steps and strict quality control. The following is a detailed introduction to its production process:
Raw material selection
Organic compounds:
The raw materials of pharmaceutical intermediates usually include various organic compounds, which are the basis for the synthesis of more complex molecules.
Inorganic compounds:
In addition to organic compounds, some inorganic compounds are also used as raw materials, which play a key role in specific chemical reactions.
Natural products:
In some cases, natural products are also used as raw materials, especially when producing intermediates with specific biological activities.
Synthesis process:
Condensation reaction: Through condensation reactions, smaller molecules are connected to larger molecules, an important step in building complex drug structures.
Oxidation reaction:
The oxidation reaction introduces oxygen atoms into molecules, which is essential for the synthesis of certain drug intermediates.
Reduction reaction:
The reduction reaction removes oxygen atoms or adds hydrogen atoms to molecules, helping to form specific chemical bonds.
Esterification reaction: Esterification reaction forms ester bonds in molecules and is a key step in the synthesis of many drug intermediates.
Purification technology
Filtration:
Physical methods are used to remove suspended particles and impurities in the solution to improve the purity of the product.
Distillation:
It is a common purification method to separate mixtures by using the difference in boiling points of different substances.
Crystallization:
The product is precipitated from the solution by changing the temperature or solvent conditions to obtain purer crystals.
Chromatography: Chromatography can efficiently separate different components in a mixture and is often used in fine purification processes.
Analytical testing
Spectral analysis:
Spectroscopic technology is used to analyze the chemical composition and structural information of the sample to ensure product quality.
Chromatographic analysis: Chromatographic analysis can accurately determine the content of each component in the sample, which is essential for monitoring the production process.
Mass spectrometry:
Mass spectrometry provides detailed information on molecular mass and structure, which helps confirm the product’s molecular structure.
Scale-up production
Optimize reaction conditions:
Based on laboratory scale verification, adjust and optimize reaction conditions to adapt to large-scale production.
Expand equipment scale: Select appropriate production equipment according to production needs and perform corresponding scale-up operations.
Ensure stable quality:
Implement strict quality control measures throughout the production process to ensure the quality consistency of each batch of products.
Packaging and storage
Select appropriate packaging materials:
Select appropriate packaging materials according to the characteristics of the product to prevent contamination and deterioration.
Control the storage environment:
Maintain appropriate temperature and humidity conditions to extend the shelf life of the product and maintain its stability.
In general, the production process of medical intermediate materials is a complex system engineering involving multiple links. Each step requires precise control and strict management to ensure the safety, effectiveness and quality standards of the final product. With the advancement of technology and changes in market demand, this field will continue to face new challenges and opportunities.